决策树是一种十分常见的分类方法,是一种监督学习。
监督学习:take examples of inputs and outputs to learn and train an algorithm, then give a new input, use this algorithm to predict an output.
监督学习可以分为classification与regression。classification与regression的分类与input无关,与output有关
- 如果output是连续的,就是regression
- 如果output是离散集合,就是classification
classfiction 与 regression的比较见如下表格:
| Input | Output | classificaction or Regression |
|---|---|---|
| Credit history | lend money or not | classification |
| a picture of person | high school, college or graduate | classification |
| a picture of person | age(float) | Regression |
一些概念
- training set
- 就是一些input,被打好标签(label)。就是一个集合,集合中的item拥有正确的input,output对。
- test set 测试集:
- 通过training set训练出一个算法,然后运用到test set中,算法获取的output与真实output比较,查看效果
- candidate:
- 只有input,output需要通过算法获取。
training set和test set不能一样
决策树
20 questions
20 questions 是一个游戏,一个人脑海中想象一个事物,另一个人通过20个是非问题来确定这个事物是什么。
策略:
- 最开始问的问题需要尽可能缩小范围,如果最开始问的就是具体问题,如果回答“否”,则基本获取不到信息。
- 问的问题的顺序可能不能颠倒。因为你下一个问题取决于上一个问题中获取的答案。
算法
- Pick best Attribute
- Best: roughly split things in half
- asked question
- follow the answer path
- go to 1
- until got an answer
ID3算法
Loop
- A <— best attribute
- assign A as decision attribute for node
- For each value of A, create a descendent of node
- sort training examples to leaves based upon exactly what values they take on
- if examples perfectly classified, stop;otherwise, iterate over each leaves, picking the best attribute in turn.
中文解释:
- ID3算法是决策树的一种,基于奥卡姆剃刀原理,即用尽量少的东西做更多的事情。ID3算法,基础就是奥卡姆剃刀原理:越是小型的决策树越优于大的决策树。尽管如此,也不总是生产最小的树形结构。
- ID3核心思想就是以信息增益来度量属性的选择,选择分裂后信息增益最大的属性进行分裂。该算法采用自顶而下的贪婪搜索遍历可能的决策空间。
奥卡姆剃刀原理:
- 简单有效原理
- 常用于两种或两种以上假说的取舍上:
- 如果对于同一现象有两种或多种不同的假说,我们应当采取比较简单或可证伪的那一种。
ID3推荐:
- good splits at the top
- prefer correct over incorrect ones
- prefer shorter trees over longer trees
information gain公式
information gain:通过挑选特定属性获取信息量的数学方法。
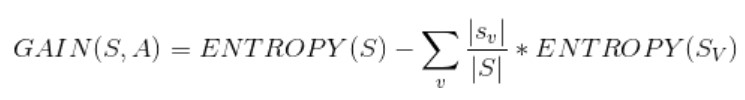
- S: 我们需要查看的训练样本的集合
- A: 特定的特征
entropy公式
entropy: 测量随机性的一种方法。
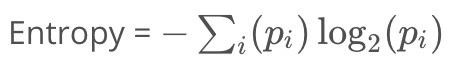
- Pi是第i类中的样本占总样本数的比例,再对所有类的结果求和
- 熵与数据单一性呈负相关
- 极端情况下,所有样本属于同一类,熵为0。在另一种极端情况下,样本均匀分布在所有类中,熵为最大值1.0。
决策树其他问题
- 何时停止
- 所有条目被正确分类后停止(若有noise,则可能无法每个条目都被正确分类)
- no overfitting
- pruning 修剪 在决策树中,通常算法overfit的原因是,这个决策树太大,太复杂。
- does it make sense to repeat an attribute along a path in the tree?
- no